VAT Invoice in Vietnam – What you need to know
In Vietnam, all organizations and individuals that produce, trade, or provide goods and services are subject to Value-Added Tax.
Currently, there are many FDI enterprises investing and doing business in Vietnam but they do not fully understand the VAT regulations. Let’s find out about Value-Added Tax in Vietnam with TOPA.VN through this blog post!

Nội dung
1. Difference Between Invoice and VAT Invoice
When an organization or individual sells goods or provides services, the seller must issue VAT Invoice for the buyer.
To be accepted by the Tax authority, VAT Invoice issued must be reasonable, strict and in accordance with the provisions of the law and the financial agency.
Furthermore, any company or person that imports goods or purchases services from overseas also needs to pay VAT.
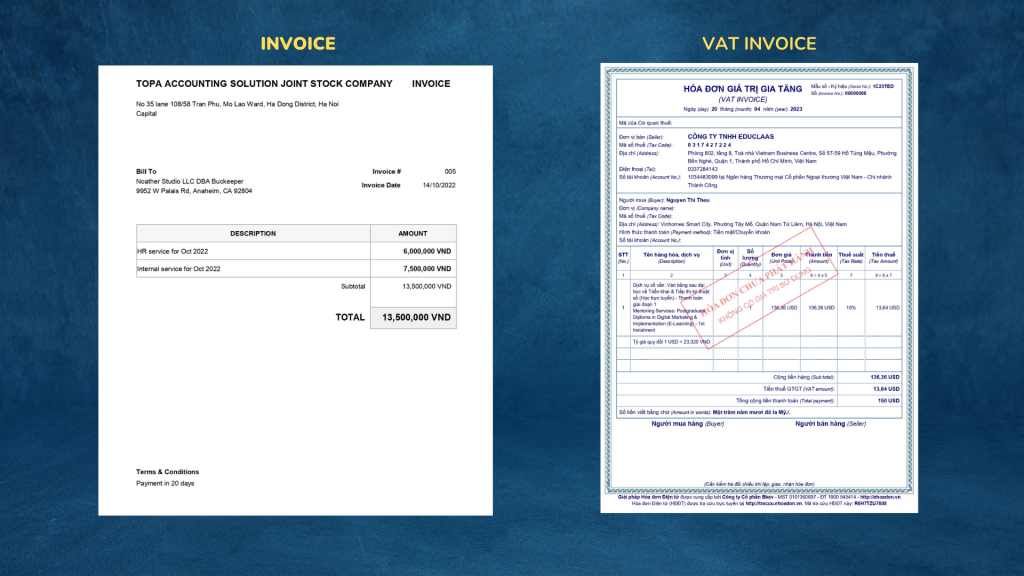
Compare Invoice vs. VAT Invoice
| Basis of Comparison | Invoice | VAT Invoice |
| Definition | – Document showing amount payable | – Document showing the details of a taxable supply and all related information as prescribed by VAT law. |
| Design | – Usually not according to any standard, the company designed by themselves | – Must comply with the regulations of the Tax authorities |
| Contents | No tax | Contains Value-Added taxes |
Information on invoices vs. information on VAT invoices
| Information | Invoice | VAT Invoice |
| Your business: your business name, registered address and Company Registration Number (if you have one) | ✔ | ✔ |
| Your customer: your customer’s name, address and contact details | ✔ | ✔ |
| The invoice: a unique invoice number, the date of issue and the word ‘Invoice’ | ✔ | ✔ |
| The items sold: unit prices, quantities, any discounts provided and the total amount due | ✔ | ✔ |
| Tax Identification Number of Business | ✔ | |
| The code on the invoice issued by the tax authority | ✔ | |
| The VAT rate(s) charged | ✔ | |
| The total amount before VAT | ✔ | |
| The total amount of tax due | ✔ | |
| The total amount due including VAT | ✔ |
2. Cost accumulation and expenses legalization in Vietnam
Businesses have a lot of expenses, but not all expenses are considered reasonable and valid for deduction when paying corporate income tax.
In Tax Accounting in Vietnam, only reasonable expenses are recognized. Otherwise, not only will you be excluded, but you may also be fined by the Tax Authority.
The company’s expenses in Vietnam:
- 90% of companies will need VAT invoices of businesses or business households as reasonable expenses
- To get the tax authorities to accept these expenses, businesses will need to prepare documents proving reasonable expenses.
- Not all expenses are recognized. Before spending any money, you need information from a tax consultant to guide problem solutions.
3. What expenses in Vietnam may not need VAT Invoice
Some Expenses without VAT, such as:
- Salary and wages for employees
- Fixed asset depreciation
- Bank interest expenses
- Rent house or rent car (of individuals)
- Outsourcing expenses such as: Hiring transportation, hiring on a case-by-case basis, contracting outsourcing, hiring labor are all deductible if there are full contracts and payment documents.
- License tax
- Social insurance expenses
These are the cases when the purchase does not need a VAT invoice. However, in order to put these costs into reasonable expenses and be accepted by the tax authorities, enterprises need to have a complete set of payment documents in accordance with regulations.
4. Other costs or expenses paid by company bank account without VAT Invoice in the accounting records
In the process of operating in Vietnam, businesses choose to pay cash or pay by bank account. How are payments made by bank accounts without invoices?
These expenses must comply with the law to be recognized. Otherwise these expenses will be counted as excluded expenses, and the business will lose money
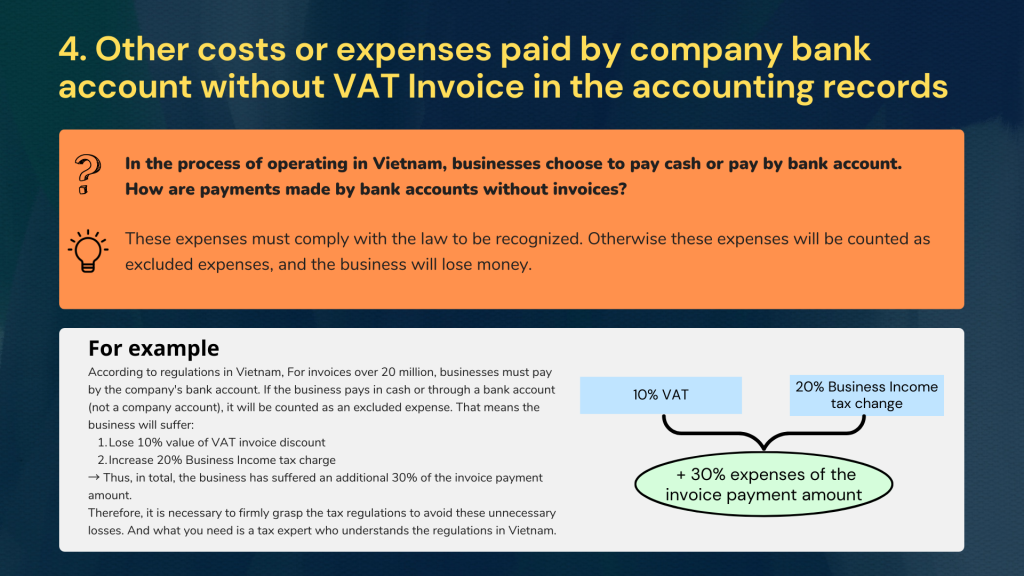
- For example:
According to regulations in Vietnam, For invoices over 20 million, businesses must pay by the company’s bank account. If the business pays in cash or through a bank account (not a company account), it will be counted as an excluded expense. That means the business will suffer:
- Lose 10% value of VAT invoice discount
- Increase 20% Business Income tax charge
→ Thus, in total, the business has suffered an additional 30% of the invoice payment amount. Therefore, it is necessary to firmly grasp the tax regulations to avoid these unnecessary losses. And what you need is a tax expert who understands the regulations in Vietnam.
LEAVE YOUR SERVICE CONSULTATION REQUEST AT OUR WEBSITE: TOPA.VN OR CALL HOTLINE 088 800 5630
>> Learn More:
REPORT LIST AND DEADLINES SUBMISSION FOR TAX DEPARTMENT & DPI OF FDI COMPANY IN VIETNAM
PROCESS TO BUY USB DIGITAL SIGNATURE TOKEN & ELECTRONICS INVOICE



























